Connection failed. What should I do?
What users need to know
For what purpose would you like to connect to the machine?
- Using a graphic application program of the remote device: Xmanager required
- Using text-based application program of the remote device (terminal access): Xshell required
- Sending/receiving files with the remote device: Xftp required
If you are not a system administrator, you should contact your system administrator to understand the following:
- The hostname or IP address of the device to be accessed
You need to know the hostname or IP address of the device you want to connect to. Xshell supports both IPv4 and IPv6. Check with your system administrator to see if you can connect by hostname. If you can only use an IP address, you need to know the IPv4 or IPv6 address. - Check connection protocol
- Using Xmanager
- Check whether XDMCP is set: This is necessary to access the graphic desktop user environment of the remote device.
- Check protocols such as SSH, Telnet, Rlogin, Rexec, etc.: At least one of these is required when using Xstart sessions or when running an X application program of the remote device.
- Using Xshell: SSH, Telnet, Rlogin
- Using Xftp: SFTP, FTP
- Using Xmanager
- Check the connection port according to the protocol
Depending on your security policy or internal use environment, a port other than the default port may be used. You should check this with your manager.
The default ports of the most commonly used protocols are as follows:- XDMCP: UDP 177
- SSH: TCP 22
- Telnet: TCP 23
- SFTP: 22
- FTP: 21
- User authentication information
You must verify the ID and authentication methods allowed for the users of the server. - Check authentication method
In the past, access was allowed only with a user password, but in recent years, other authentications such as interactive passwords, software or hardware key authentication, etc. are commonly used instead or are used in parallel with passwords.
You should check with your system administrator.
Once you have confirmed the information of the above 5 points, you can try to access the server with the program that is suitable for your purpose.
Solutions by failure type
The following are common cases of connection failure that can occur in Xshell.
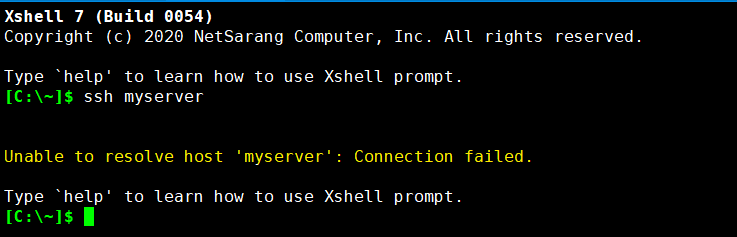
- Unable to resolve host '...': Connection failed
In this case, the server hostname could not be resolved to the IP address. It is either not registered in DNS or the company name service system, or the user entered the wrong name.
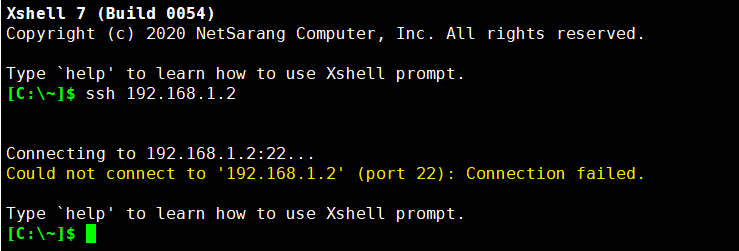
- Could not connect to '192.168.1.2' (port 22): Connection failed.
This may occur when attempting to connect to 192.168.1.2 (example) using the SSH protocol.
The reasons for the above message can be one or more of the following.- Connection to the IP address is not possible due to a firewall or network environment
- The SSH protocol is not available
- The SSH protocol is set, but the port is set to a port other than the default port
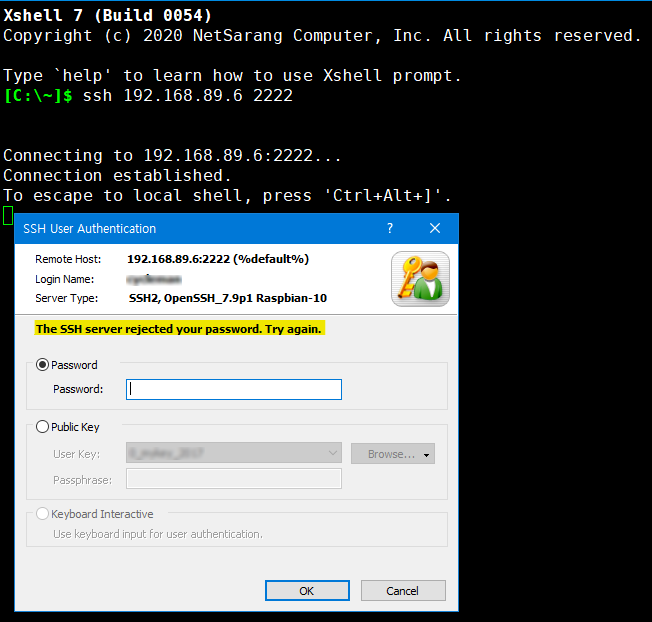
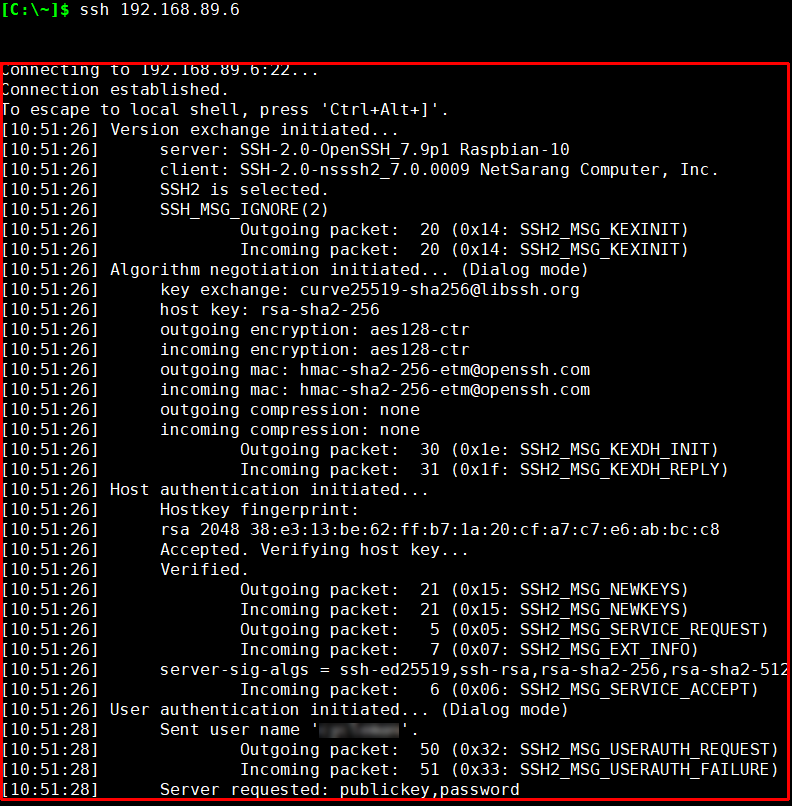
- The SSH server rejected your password. Try again.
With the help of the administrator, the connection was successful by verifying the SSH server's IP address and connection port. However, there is a problem with the entered username and password, and the final connection has failed.
The reasons for the above message can be one or more of the following.- The user does not exist or the name is incorrect
- The password was entered incorrectly
- The SSH server does not accept password authentication. In this case, you will need to contact the server administrator to confirm which authentication methods are allowed and to obtain an authentication file or hardware token associated with the appropriate authentication method.
If you cannot connect due to an unknown reason
In this case, make a technical support request to NetSarang Computer's technical support team.
For the quickest turnaround, include the following information when making your request:
- OS type and version of the device being connected to
- Connection protocol
- Screenshots of the issue
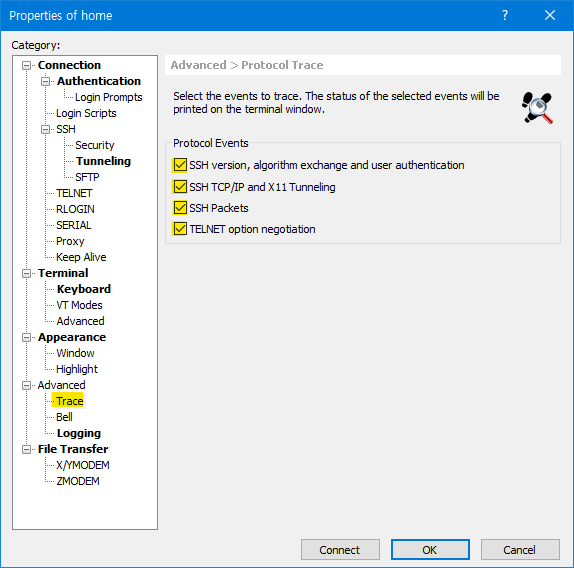
- Access log after turning on the trace features of the protocol